This article is about the side effects of Blood cancer. In this article, we will discuss the types of blood cancer, symptoms of blood cancer, sides effects of blood cancer and mainly the Long Term Side Effects Of Blood Cancer.
Blood Cancer
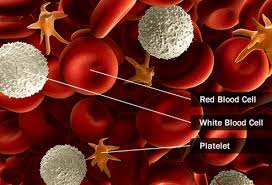
Blood cancers effect in a systemic way as they affect the whole body. It affects your blood cell’s production and functions. Mostly, these types of cancers start in your bone marrow where blood is created. Stem cells mature and developed into three types of blood cells:
- A myeloid stem cell matures into a myeloid blast which can form a Red Blood Cell
- One of several types of White Blood Cells.
- or platelets.
Types of Blood Cancers
In most blood cancers, the uncontrolled growth of an abnormal type of blood cell interrupts the normal blood cell development process.
Blood cancer is an umbrella term which is for cancers that affect the blood, bone marrow and lymphatic system. This is the type of cancer, which is the fifth largest group of cancers in the UK and includes:
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Myeloma
Leukemia:-
Leukemia is cancer which starts usually the bone marrow (in blood-forming tissue) and causes the making of large numbers of abnormal white blood cells (which help in defending the body against infection).
These abnormal/cancerous cells cause hurdles in carrying out the normal functions to white blood cells.
Types of Leukaemia:
There are three types of lymphocytes,
- B lymphocytes that make antibodies to
fight infection - T lymphocytes that help B lymphocytes
- Natural killer cells that attack cancer cells
and viruses
Leukemias are titled after the type of blood cells involved. Those which involve the granulocytes, red blood cells, platelets and monocytes are called myeloid leukemias. those which involve the lymphocytes are called the lymphocytic leukemias.
Four main types of leukemia:
- Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) – AML starts in the bone marrow and moves into the blood. Afterward, it spreads into other parts of the body including the liver, brain, and spinal cord and testicles. Acute Myeloid Leukaemia is caused by the production of too many immature white blood cells in bone marrow, by the stem cells. These immature white blood cells are named as blast cells.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) – when the body makes too many lymphoblasts, a type of white blood cell, it causes acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). It can affect the person of any age but most commonly, it is found in the kids of the aged 2-5 years.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML) – It causes the body to make too many white blood cells. patients, who are affected by CML, produce too many granulocytes and other myeloid cells.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL) – A type of slow-growing leukemia that affects developing B-lymphocytes, a specialized white blood cell.
Recommended: Natural Ways to Cure Cancer
Lymphoma:-
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the cells which are the part immune system of the body. If you’ve Lymphoma cancer, you must know what type of Lymphoma cancer is it because it affects your treatment options and your prognosis.
If you have Lymphoma, you may feel the lymph nodes in the:
- neck
- upper chest
- armpit
- stomach
- groin
And the common early symptoms of lymphoma include:
- bone pain
- a cough
- fatigue
- enlarged spleen
- fever
- night sweats
- pain while drinking alcohol
- itchy rash
- rash in skin folds
- shortness of breath
- skin itching
- stomach pain
- unexplained weight loss
Types of Lymphoma:
There are two major types of Lymphoma cancer:
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HD):-
Once it starts making progress, it makes it difficult for the body to fight with the infection.
In people, who are affected by HD, infected white blood cells grow abnormally and spread beyond the lymphatic system.
HD can be of two types. Either of classic Hodgkin’s disease or of nodular lymphocytic predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NLPHL). The type of HD is based on the types of cells involved in the patient’s condition and their behavior.
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma:-
A type of blood cancer by which, the lymphatic system is affected.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma usually starts in a lymph node at one or more than one body parts. It spreads from one lymph node to another. It can also spread to the bone marrow, spleen and liver.
Sometimes, non-Hodgkin lymphoma starts in the stomach, bone, skin, brain and spinal cord. This process is known as extranodal disease.
Myeloma:-
Myeloma, also known as multiple myeloma, is cancer which forms in mature white blood cells, called plasma cells. Plasma cells produce special proteins, known as antibodies or immunoglobulins, which help to fight infection.
Types Of Myeloma:
Myeloma is classified on the basis of its affections. In a majority of patients, infection affected in multiple bone marrow sites at diagnosis. In this case, the disease is called multiple myeloma.
It can also be classified by the type of immunoglobulin being secreted by the myeloma cells, and its affection on the body.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of Myeloma are:
- Anaemia, tiredness, fatigue, weakness, and dizziness
- Increased bleeding or bruising
- Bone pain
- Elevated blood calcium level
- Frequent or repeated infections
Types Of Blood Cancer Treatments And Their Side effects
Types:
- Stem cell Transplantation
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
Stem cell Transplantation:
when stem cells have been damaged or destroyed by disease, a stem cell transplant is used to replace them.
Side Effects:
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
- belly pain
- Weight loss
- Mouth and throat pain
- lung problems
- Graft-versus-host disease
- Bleeding and transfusions
Chemotherapy
In this treatment, a wide amount of drugs is used to kill cancer. Its effectiveness depends on the stage of cancer.
Side effects:
- Mouth and throat sores
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Blood disorders
- Weakness or numbness in the hands, feet, or both
- Shaking or trembling
- Loss of balance
Radiation therapy:
It is a local treatment, aimed at and affects only the part of the body which is being treated. The main moto of radiation treatment is to damage cancer cells.
Side effects:
- Skin problems
- Fatigue
- Dry mouth
- Mouth and gum sores
- Difficulty swallowing
- Stiffness in the jaw
- Nausea
- A type of swelling called lymphedema
- Tooth decay
Long-Term Side Effects
Heart Problems
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy to the chest can cause heart problems. Survivors who are expected to have a higher risk include:
- Those who received treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma in childhood
- Anyone aged 65 and older
- One who received higher doses of chemotherapy
- Those who received medicines, such as trastuzumab and doxorubicin
Hypertension
If you have a blood pressure problem, you must talk to your doctor. You may need to track your blood pressure more closely during cancer treatment.
Ask your doctor if you’re using any of the following medicines:
- Bevacizumab (Avastin, Mvasi)
- Sorafenib (Nexavar)
- Sunitinib (Sutent)
Lung problems
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy to the chest can damage your lungs.
Cancer survivors who received both chemotherapy and radiation therapy are more likely expected to have a higher risk of lung damage. Some of the drugs that may cause lung damage include:
- Bleomycin (Blexane)
- Carmustine (Becenum, BiCNU, Carmubris)
- Methotrexate (multiple brand names)
The effects may include the following:
- A change in how well the lungs work
- Thickening of the lining of the lungs
- Inflammation of the lungs
- Difficulty breathing
Bone, joint, and soft tissue problems
In the medical field, there’s a term used, osteoporosis, which is, thinning of the bones, or joint pain. Steroid medications, chemotherapy, or hormonal therapy may cause osteoporosis. To reduce the risk of these conditions, survivors must be physically active.
Survivors can reduce the risk of osteoporosis in these ways:
- Avoiding tobacco products
- Eating foods which have a high quantity of calcium and vitamin D
- Becoming physically active
- Limiting the use of alcohol (if any)
Brain, spinal cord, and nerve problems
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy can cause long-term side effects to the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The late effects include:
- Hearing loss from high doses of chemotherapy, especially drugs like cisplatin (multiple brand names)
- Increased risk of stroke from high-dose radiation therapy to the brain
Digestion problems
Both, chemotherapy and radiation therapy and surgery may affect the digestive system of a person. Surgery to the abdominal area may cause tissue scarring, long-term pain, and intestinal problems which may affect digestion.
Emotional difficulties
Survivors often experience various positive and negative emotions, which include:
- Relief
- A sense of gratitude to be alive
- Fear of recurrence
- Anger
- Guilt
- Depression
- Feeling alone


Comments are closed.